Cannabinoids and You: A Crash Course On What’s Inside Cannabis
Cannabis, for thousands of years, has been used for medicinal purposes all around the world. Without cannabinoids though, cannabis wouldn’t be very medical at all. Check out this crash course to learn how the specific chemicals that work to provide cannabis’ many medical properties. While many medical cannabis beginners may know a few distinctions, like indica vs. sativa, even cannabis enthusiasts may not know every compound that makes up the plant. There are 66 different known cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, and a good deal have medical properties. Taking the time to get a basic knowledge of cannabinoids can help you better understand why medical cannabis has such a large range of efficacy for treatment and remedy options for patients. The guide below will outline some basic cannabis chemistry.
Cannabinoid Crash Course
Making Sense of the Endocannabinoid System
Why does cannabis have such distinct medical effects? It’s all thanks to your body’s endocannabinoid system (EC). Your body has a system of receptors that, when binded to, produce medicinal effects. Only cannabinoids can bind to these EC receptors, which is the culprit behind cannabis’ power. Normally your endogenous, or internally made, cannabinoids bind with these receptors to produce natural effects on pain, appetite, and memory. These natural cannabinoids though, cannot fight the battles on their own.
When you consume medical cannabis, its cannabinoids bind to EC receptors in the brain, CB1, and in the body, CB2. The different cannabinoids will bind to these different receptors, creating distinct effects which we will discuss in detail below. The important takeaway for patients is medical strains can be cultivated to maximize certain cannabinoid effects, thus creating more efficacious, personalized medicine.

The THC Class
While THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the most popular and well-known cannabinoid. There’s actually a few different types of THC present in medical cannabis.
- THCa, which becomes THC when combusted, and
- THCv
Both bind to CB1 receptors, most commonly found in the brain. THC, the end product of THCa, produces the psychoactive effects associated with cannabis. When we think of euphoria and elevated mood produced by medical cannabis, we must give credit to the THC class of cannabinoids. Check out more in-depth detail of each THC cannabinoid below.

THCa
THCa is why medical cannabis must be dried and cured following cultivation. When cannabis flowers are freshest, pre-cure process, they are very slick and sticky, coated in THCa. If one were to combust this live cannabis, they wouldn’t receive many benefits. As the plant is cured the THCa slowly turns into THC, and then when combusted or vaporized it will provide users with THC’s benefits. THC has anti-inflammatory properties, provides pain relief, can curb nausea and inhibit cancers growth. For more medicinal effects, the higher the THCa the better. Most medical cannabis strains have high levels of THCa, like Theory Wellness strains, which provide an average of more than 24% THCa.
THCv
THCv is very similar to THC, in fact, it’s only molecular difference is a 3-carbon side chain, depicted above. THCv will cause euphoric sensations, much like THCa, but these are often described as more intense. This causes a stimulation of energy that can help those who need invigorating effects to take on the day, while also providing some relief for depression. The biggest difference between THCa and THCv is their properties when it comes to appetite. THCv has been found to produce an appetite suppressant effect. While medical cannabis may give patients improved appetites, THCv is thought to be the reason why most cannabis users are skinnier on average. High levels of THCv tend to be found in strains of African descent.
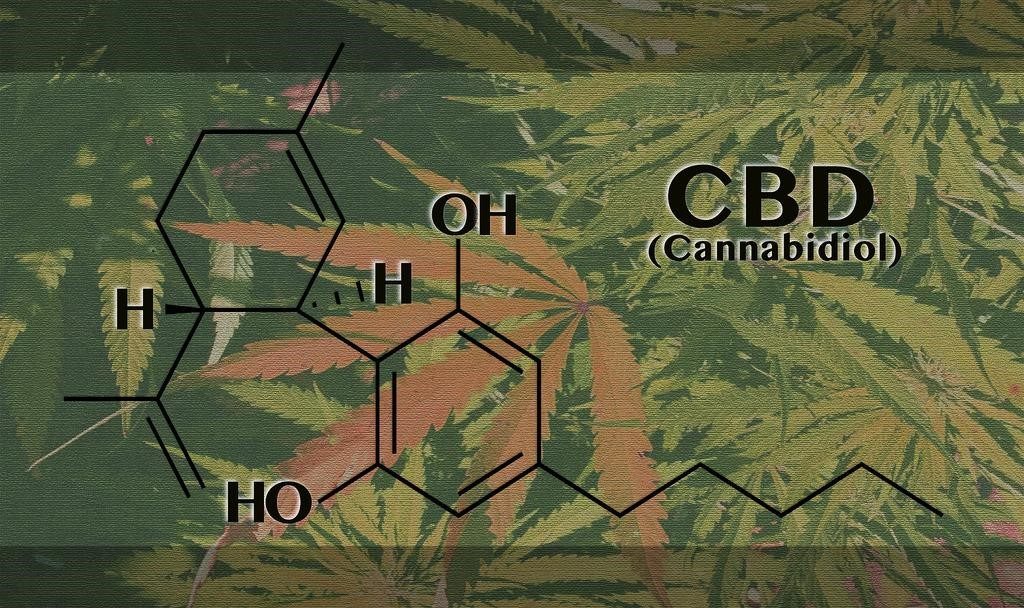
The CBD Class
Of any cannabinoid, CBD may be the most abundant in cannabis flower, making up almost half of the combusted cannabis resin. CBD, and similar cannabinoids house much of cannabis’ medical properties, like anti-anxiety, inflammation, pain, nausea, as well as fighting seizures for people who suffer from epilepsy, without the psychoactive effects. With the benefits and being nationally legal, CBD has become an almost billion dollar industry. In fact, one of the first ever primarily CBD strain, Charlotte’s Web, was created for a little girl suffering from epilepsy.

CBDa
CBDa becomes CBD when combusted, vaporized, or consumed in an infusion. CBD is lauded for its stability. When you ingest CBD, you don’t feel any chemical effects akin to a “high” or what we call euphoria from THC. These benefits include relief from epilepsy, pain management, and anti-inflammation. This makes CBD rich strains a go-to for child patients, as well as patients who seek medication during the workday. Moreover, CBD can be used in many different forms. We even offer a CBD canna-salve that allows patients to get topical relief for skin areas where inflammation or pain are present.

CBGa
CBGa becomes the cannabinoid CBG when combusted, vaporized, or consumed in an infusion. This compound has been found to contribute to cannabis’ efficacy for treating glaucoma, as well as inhibiting tumor growth. What we know most about CBG is that it helps our muscles relax, and can lower inflammation. This pair of actions make it an effective sleep aid, and strains that have higher amounts of CBG tend to be less head heavy and more relaxing. Right now, Theory Wellness offers Star Flight Guava, a strain that is made up of 0.5% CBGa.
You can take a look at all of our strains individual cannabinoid levels here. Taking the time to compare cannabinoid levels may help you find the strain or remedy that is right for you and your medical cannabis experience. We are eager to help any patient find the perfect strain for their desired benefits, and we utilize our knowledge of cannabinoids to do so effectively.




